The Coal Authority has issued the Aberpergwm coal mine with a licence to mine an extra 42 million tonnes of coal, ignoring the est.100 million tonnes of CO2 this will generate and jeopardise the UK's and Wales' ability to meet their climate commitments. Check out what we're doing now to stop the Aberpergwm coal mine expansion.
Currently, the Welsh Government and the UK’s Government Ministry of BEIS are arguing over which has the legal power to cancel the impending licence for a coal mine extension in Aberpergwm, south Wales. EnergyBuild Ltd, the coal operator, is on the brink of getting a licence to extend an existing deep coal mine to extract a further 40 million tonnes of coal, emitting around 100 million tonnes of CO2 and methane, until 2039. The licence could be obtained any day, and work begin shortly thereafter (we’ve illustrated the main legal steps a coal mine takes between application and diggers on the land). This is a very live issue.
Demand Ministers block this coal mine extension now.
The governments of Wales and the UK both believe that the other has the power to stop the coal mine extension from going ahead. In the meantime, and in the shadow of the recent COP26 in Glasgow, a licence to extract a further 40 million tonnes of coal could slip through any day. The estimated 100 million tonnes of CO2 and methane this would emit over the next 18 years, would discredit the much-boasted 2050 Net-Zero commitment, Boris Johnson’s recent statement in the press against new coal, and the Welsh Ministerial statement against coal in March 2021. The signal this may send to other world leaders, that they can make commitments then ignore them, is hard to quantify but may be even more significant. Ministers Lee Waters of the Welsh Government, and Michael Gove of the UK Government, need to come together to stop this coal mine and make good on their respective governments' climate commitments.

The distance between the coal mine and the nearest residence in Aberpergwm is just 330 metres. Although this is a deep coal mine rather than opencast, this proximity can still be associated with impacts from coal dust from coal stockpiles stored above ground, noise, HGV movements, and light pollution. Future impacts of the underground working are also uncertain with increasingly extreme weather events associated with climate change.
For people living in many parts of the Global South, on flood planes, or near sea-level, climate change is not an abstract threat for future generations – it's impacts are life and death, and are experienced now and locally to them. The line between who we think of as ‘local communities’ is beginning to blur as the impacts are increasingly experienced beyond the site of operations. The economic and health impacts of the coal mine extension going ahead or closing will be immediate, direct, and tangible on the residents in Aberpergwm. The impacts of the CO2 and methane from this coal mine will be delayed, indirect, and, although modelling tools attempt to quantify it, fairly intangible on communities threatened now by climate change. However, the consequences are profound for both groups, and must be considered.

Cutting through the greenwash, a significant portion of the coal will be burned at steelworks releasing huge amounts of CO2 and other pollutants, jeopardising the rapid decarbonisation required of the global steel industry and other industries which are reliant on coal.

A visit to Companies House online will reveal a complicated operating structure of many small companies with similar names and shared registered addresses associated with Energybuild Ltd, the coal operator in Aberpergwm. The company itself has negligible assets, so the possibility of recovering funds if the company suddenly folded with liabilities is limited. The situation with its holding company, Energybuild Resources Ltd is also concerning, with net liabilities of £2.7 million and assets valued at £950 thousand as of the end of 2019 – meaning that if the company were to fold, around 65% of those liabilities may not be fulfilled, including restoration works.
Wales played a major role in mining the coal that powered the UK through an industrial revolution. Coal is a central part of a proud heritage in many communities throughout Wales, and for a few remaining areas, coal mining is still the major industry.
The closure of many coal mines under the Thatcher Government put thousands out of work, generating bitterness and deprivation that continues to this day. Much of this hardship could have been avoided if coal mining had been phased out and replaced by reinvesting some of the wealth that mining generated back into the communities that toiled to extract it.
Local shops and pubs, in particular, in recent press coverage have come out in support of a licence for the coal mine extension, highlighting their reliance on the custom of coal miners that work there. But without the support for creating alternative jobs that’s been absent so far, these businesses will be in the same position when the coal mine does eventually close.
Will the UK Government learn from its past mistakes in coal, and make good on its promise to ‘level up’ the UK with an approach that includes investment in infrastructure, retraining in desirable and viable jobs, and financial support for small and medium sized enterprises, particularly cooperative and social-interest companies that build and reinvest in their communities? Only when the UK and Welsh governments step up will communities in Aberpergwm have a genuine choice on whether to tolerate a coal mine nearby for another 18 years.
The Aberpergwm extension may represent the final gasps of an industry we owe much to but must move beyond. As one tenacious community member fighting a coal mine near Newcastle put it, "coal is our collective heritage, but it cannot be our future".
Following almost 4000 emails, we've followed up with an open letter to Ministers Lee Waters and Michael Gove.

16 years of opencast coal mining in Ffos-y-fran has generated colossal overburden mounds, also known as slag heaps or coal tips. There are three coal tips, with the third being the largest, and cumulatively accounting for 37 million cubic metres of colliery spoil, rocks, and soil…

We were invited for the second time to give oral evidence to the Climate Change, Environment, and Infrastructure Committee of the Welsh Parliament (Senedd) on 05th February 2025. We shared the panel with Haf, Director of FOE Cymru, to provide our opinion on the weaknesses, strengths…
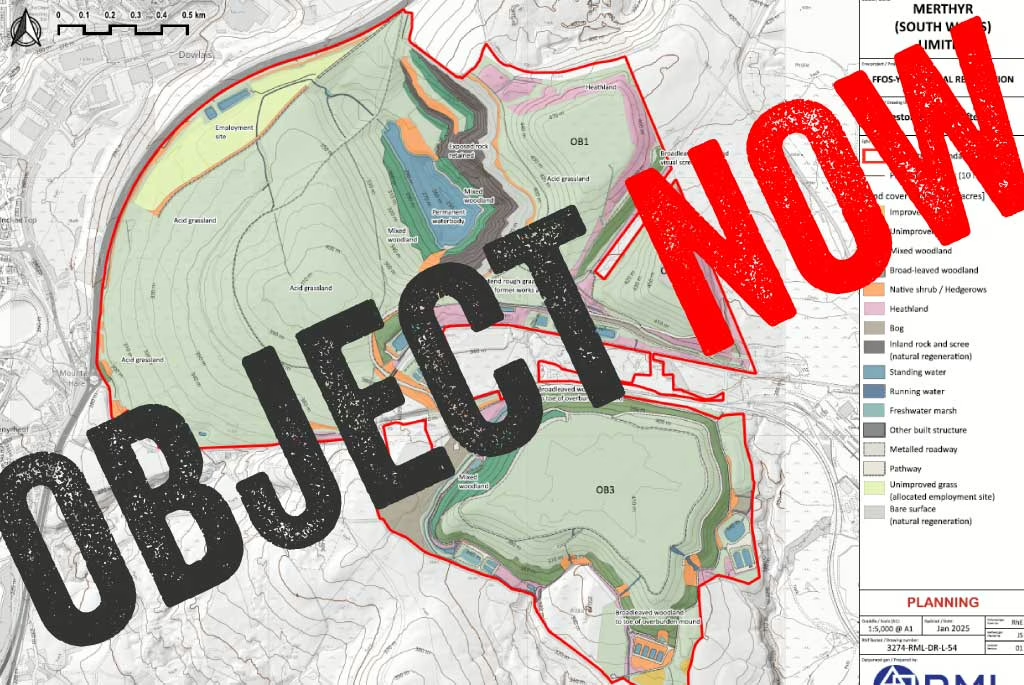
Merthyr (South Wales) Ltd mined for over a year illegally after planning permission for the Ffos-y-fran opencast coal mine ended in September 2022. During that year, it made record-breaking profits due to sanctions on Russia and other factors driving up the price of coal. But rather than using some of the profits from that ill-gotten coal…

MSW claims “It was established that there are insufficient funds available to achieve the 2015 restoration strategy and therefore an alternative scheme is required.” (EIA Scoping Report, July 2024)… To our knowledge, there has been no evidence submitted by MSW that it cannot fund the full restoration it is contracted to undertake…

The UK Government launched a consultation on a limited review of the National Planning Policy Framework (NPPF) for 8 weeks from 30 July to 24 September 2024. The NPPF is an influential document that shapes planning decisions and priorities across England. It is periodically updated by the Government, following a public consultation…

Bryn Bach Coal Ltd attempts to present the anthracite coal it wishes to extract from an expansion of Glan Lash as a unique and scarce commodity that is needed for water filtration, bricks, and graphite, and would therefore be too valuable to burn. Yet, visiting Energybuild Ltd’s…

Over the past year, we’ve secured some massive victories. By taking part in our digital actions, supporters sent over 26,000 messages to the UK Government, MPs, Welsh Senedd members, Councillors, and companies to help consign coal to the history books in the UK…

The Disused Mine and Quarry Tips (Wales) Bill (‘the Bill’) was prompted by a series of coal tip landslides that occurred in Wales following storms’ Ciara and Dennis in 2020, including a major landslide of a disused coal tip in Tylorstown…

As B Labs doesn’t seem bothered was the public says, we asked supporters to contact other B Corps – who are effectively B Labs customers. Almost 20,000 emails were sent to over 60 B Corp status companies, asking them to take a stand with us…