
EMR Capital, the company that owns 81% of the proposed West Cumbria Coal mine, is currently operating another coking coal mine – Kestrel.
The Kestrel mine is an underground mine located in the Bowen Basin in central Queensland. The Bowen Basin contains the largest coal reserves in Australia.
The mine produces twice the annual output proposed for West Cumbria, at 5.56 million tonnes a year. The Kestrel coal mine is not without controversy, which could occur in West Cumbria if the mines started. See below for recent issues for workers, subsidence and with polluted water discharge which at Kestrel could affect the Great Barrier Reef or the coast at Cumbria.
There is not a strong campaign focus against Kestrel coal mine specifically, as in 2021, Australia had 94 operational coal mines, coal and a much lower population density than in the UK. The mine has operated since 1992.
Like the proposed West Cumbria Coal mine, Kestrel is not owned and operated by just one company.
Kestrel mine is owned by Kestrel Coal Resources (80%) and Mitsui Investments (20%). Kestrel Coal Resources is made up of 52% EMR Capital, with Adaro Capital Ltd owning the other 48%.

Location of Kestrel coal mine
Key facts

Protests and disputes
There were workers disputes at the mine in 2022 over job contracts, including redundancy policies, health insurance policies and our incentive bonus policy. The Mining and Energy Union vice president criticized Kestrel over the ongoing saga. [10]
The mine was for sale in 2022. It does not seem to have found a buyer.
Threat at a local level
The traditional owners of the land are the Western Kangoulu people who co-operate to some extent with the miners, but say “the sectors activities also present a large threat to the protection of cultural heritage and values with extensive and irreparable damage being done to the land resources of the Western Kangoulu area.” [11]
Environmental issues
Lock the Gate has highlighted that “Central Queensland coal mines are releasing billions of litres of polluted water many times saltier than the receiving rivers in the catchment of the Great Barrier Reef, prompting concerns about the ecological health of impacted waterways.”
According to the Environment Department’s figures, Kestrel, in Jan 2023 was releasing the equivalent of an Olympic-sized swimming pool of water every eight seconds into Crinum Creek.
The Environmental Advocacy in Central Queensland director said, “It’s particularly galling that even coal mines that publicly claim to be ‘zero-discharge’, such as Kestrel, are releasing thousands of litres into Central [Queensland] creeks every second which will be carrying sediment to the Reef.” [12]
Subsidence
There has been subsidence at the Kestrel mine, this was likely planned. The area over the mines is mainly agricultural. Subsidence is where the ground sinks after coal mining has cleared an underground void and the rock roof is allowed to fall in, causing disruption at ground level.
At the Kestrel mine there is recorded subsidence of 1.6m to 2 m down the centre of the 250 m wide panels. These panels are approximately 4km long.” At the Kestrel site this affects the hydrology of the area. Similar subsidence, were it to take place, at the currently proposed West Cumbria coal mine, would cause disruption on the sea bed. If this is expected a license for the mine is required from the Marine Management Organisation. As “subsidence increase[s] permeability and porosity”. [13]
1 https://kestrelcoal.com/stakeholders/
4 https://www.adaro.com/pages/read/7/22/mining
5 https://www.gem.wiki/Kestrel_mine
8 https://www.ga.gov.au/digital-publication/aecr2023/coal
11 https://lumburrabimbi.com.au/western-kangoulu/
12 https://lumburrabimbi.com.au/western-kangoulu/
13 file:///home/anne/Lechner2014Theimpactofundergroundlongwallminingonprimeagriculturalland.pdf Referencing Gullo D. 2006. Kestrel coal mine: subsidence and agriculture. Central Queensland Mining Forum. 18 October 2006. Fitzroy Basin Association, Emerald, Queensland, Australia., Booth & Spande, 1992; Potentiometric and aquifer property change above subsiding longwall mine panels, Illinois basin coalfield. Ground Water 30: 362–368., and Booth, 1998, Impacts of mine subsidence on groundwater. In Proceedings of Prime, Farmland Interactive Forum, Hooks CL, Vories KC, Throgmorton D (eds). Department of Agronomy, Illinois Agricultural Experiment Station, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, University of Southern Indiana: Evansville; 143–148.).

As part of our Politics Unspun series we are unpacking politicians’ public comments on coal to challenge any misleading or incorrect messages. Todays’ focus is on comments made during a Westminster Hall debate in December 2025 about the oil refining sector. During the debate, Lee Anderson MP made some statements about coal…

The Government is reforming planning policy in England and thanks to thousands of our supporters asking for an end to coal extraction in the last consultation in 2024, they are now recommending that planners “should not identify new sites or extensions to existing sites for peat or coal extraction”…
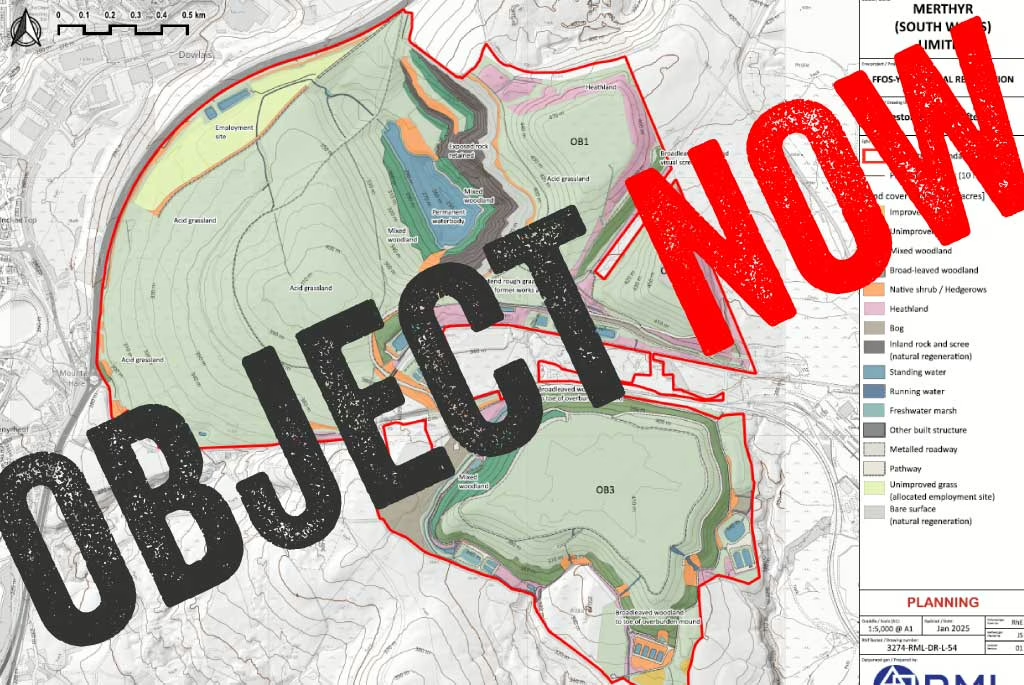
Merthyr (South Wales) Ltd mined for over a year illegally after planning permission for the Ffos-y-fran opencast coal mine ended in September 2022. During that year, it made record-breaking profits due to sanctions on Russia and other factors driving up the price of coal. But rather than using some of the profits from that ill-gotten coal…

In November 2024, the new UK Government announced its intention to legislate a ban of new coal mining licences – which we welcomed. Over a year later, the legislation is yet to be introduced, and the Government is not planning to include all types of extraction…

The UK steel and cement sectors (and to a lesser extent, bricks) are the largest users of coal following the closing down of the UK’s last coal-fired power station in September 2024. Check out our coal dashboard for our most recent coal stats including an industry break-down. We support the UK Government’s commitment to ban…

The steel industry produces 9-11% of the annual CO2 emitted globally, contributing significantly to climate change. In 2024, on average, every tonne of steel produced led to the emission of 2.2 tonnes of CO2e (scope 1, 2, and 3). Globally in 2024, 1,886 million tonnes (Mt) of steel were produced, emitting…

Last month we worked with Members of Parliament from various parties on a Westminster Hall debate about coal tip safety and the prohibition of new coal extraction licences. The debate happened 59 years and one day after the Aberfan tragedy which killed 116 children and 28 adults…

Successful, at-scale, examples already exist of cement works burning 100% fuel alternatives to traditional fossil fuels, including pilot projects using combinations of hydrogen and biomass (UK) and hydrogen and electricity (Sweden). Yet, innovations such as use of hydrogen and kiln electrification are…

Within the borders of the Senedd Caerphilly constituency is the proposed Bedwas coal tips re-mining project. In the lead up to the Senedd by-election, Coal Action Network has carried out a survey of the by-election candidates asking for their views about the re-mining of the Bedwas and other…