
On 15th September 2023, The Guardian reported that Tata Steel accepted Government funding to avoid closing its steelworks in Port Talbot, South Wales, by decarbonising it instead – but at a loss of up to 3,000 jobs.
The UK Government is providing £500 million, and Tata Steel is expected to provide another £725 million. Most of this money will go to converting the sprawling steelworks from its current Basic Oxygen Furnaces to Electric Arc Furnaces. The former produces virgin steel from iron ore, heavily relying on coal for the chemical reaction. Electric Arc Furnaces recycles scrap steel without needing coal. Currently, the UK exports a considerable quantity of scrap steel abroad (over 8 million tonnes in 2021), and scrap steel is expected to greatly increase in abundance globally.
Port Talbot steelworks is currently the 2nd highest source of CO2 from any single site in the UK. Transitioning this steelworks is expected to make a significant impact on the UK’s emissions. Steelworks around the world contribute 11% to global greenhouse gas emissions… rapid decarbonisation globally is essential to limit climate chaos and, alongside electric arc furnaces, alternatives are under development and testing that removes coal from the process of making virgin steel.
However, steelworks employ many thousands of people around the world, whose labour has been essential for everything from vehicles and renewable energy infrastructure to household appliances. It’s essential steel workers and their unions are centred in the changes needed to decarbonise steelworks to ensure a just transition that doesn’t leave these workers behind. The planned decarbonisation of Port Talbot Steelworks has been reported not to follow the principles of a just transition. Instead, the company has reportedly shut unions out of its negotiations with the UK Government and there aren’t any reported programmes of retraining or support packages to equip workers facing redundancy with realistic prospects of finding alternative work that suits their experience or ambitions.

Steel companies in Europe may be amongst the first to decarbonise their steelworks, so it is essential they set a good example for steel companies elsewhere to follow. European steelworks, therefore, must meaningfully engage with their workers and workers’ Unions from the outset of plans to decarbonise steelworks, focusing on those most impacted by potential changes. We are sceptical of top-down consultations on changes which often have foregone conclusions—engagement must be in the form of equal partners around the table. For workers, this can have the advantage of securing packages of support that are appropriate for their needs, whether that is to stay within the company or gain employment in another industry. Worker creativity may also reduce their own job losses and impacts—if they are able to meaningfully shape the transition process. Companies benefit from the creative capacity of workers who have on-the-ground expertise, greater trust in the changes ahead, reputational impacts, better worker morale and loyalty, and the wider fallout that structural unemployment can drive.
British Steel, the UK’s only other producer of virgin steel and operated by Jingye, is also considering converting its steelworks to electric arc furnaces in the hope of accessing hundreds of million in Government funding to decarbonise the steelworks. British Steel has secured a £100 million contract to build one of the world’s biggest offshore wind plants being built at Teesworks. We hope that Jingye actively involves workers at British Steel, and their unions, from the outset of any plans to transition its steelworks.

Coal Action Network is proud to present our 2026 manifesto for Wales. With the Senedd elections taking place in May this year, Wales stands at a decisive moment. For over a century, coal has shaped Welsh landscapes, communities, and politics. Today, Wales has the opportunity to shape something very different…

As part of our Politics Unspun series we are unpacking politicians’ public comments on coal to challenge any misleading or incorrect messages. Todays’ focus is on comments made during a Westminster Hall debate in December 2025 about the oil refining sector. During the debate, Lee Anderson MP made some statements about coal…

The Government is reforming planning policy in England and thanks to thousands of our supporters asking for an end to coal extraction in the last consultation in 2024, they are now recommending that planners “should not identify new sites or extensions to existing sites for peat or coal extraction”…
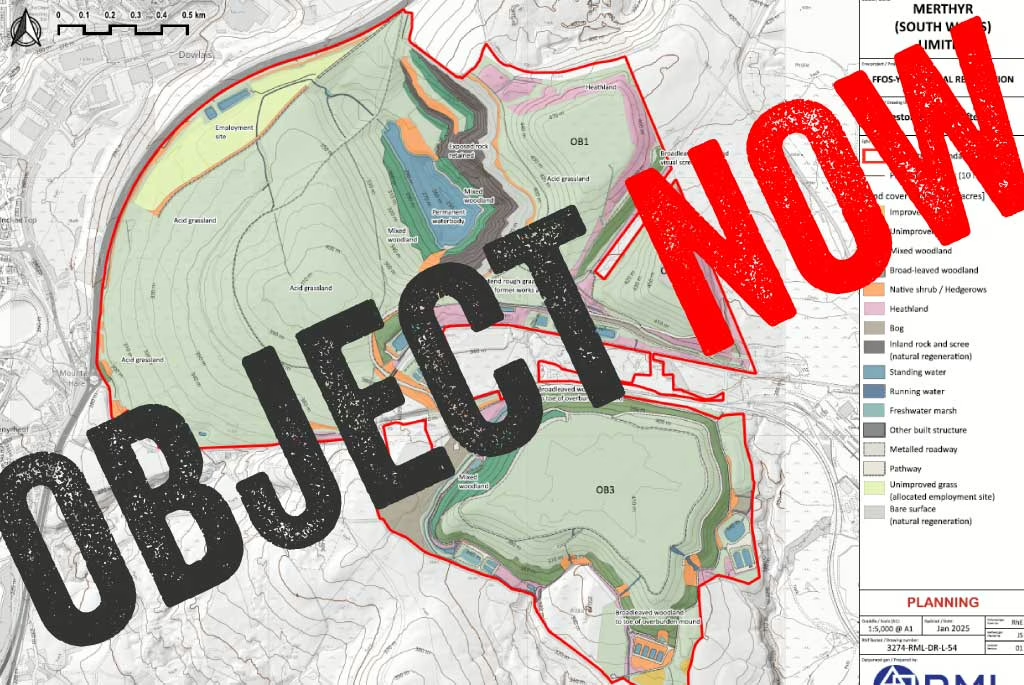
Merthyr (South Wales) Ltd mined for over a year illegally after planning permission for the Ffos-y-fran opencast coal mine ended in September 2022. During that year, it made record-breaking profits due to sanctions on Russia and other factors driving up the price of coal. But rather than using some of the profits from that ill-gotten coal…

In November 2024, the new UK Government announced its intention to legislate a ban of new coal mining licences – which we welcomed. Over a year later, the legislation is yet to be introduced, and the Government is not planning to include all types of extraction…

The UK steel and cement sectors (and to a lesser extent, bricks) are the largest users of coal following the closing down of the UK’s last coal-fired power station in September 2024. Check out our coal dashboard for our most recent coal stats including an industry break-down. We support the UK Government’s commitment to ban…

The steel industry produces 9-11% of the annual CO2 emitted globally, contributing significantly to climate change. In 2024, on average, every tonne of steel produced led to the emission of 2.2 tonnes of CO2e (scope 1, 2, and 3). Globally in 2024, 1,886 million tonnes (Mt) of steel were produced, emitting…

Last month we worked with Members of Parliament from various parties on a Westminster Hall debate about coal tip safety and the prohibition of new coal extraction licences. The debate happened 59 years and one day after the Aberfan tragedy which killed 116 children and 28 adults…

Successful, at-scale, examples already exist of cement works burning 100% fuel alternatives to traditional fossil fuels, including pilot projects using combinations of hydrogen and biomass (UK) and hydrogen and electricity (Sweden). Yet, innovations such as use of hydrogen and kiln electrification are…
The proposed changes at Port Talbot and Scunthorpe are not decarbonising steel production but ending production and moving to recycling steel. There is nothing wrong with recycling steel but it is likely that we will still need some new steel which will be produced elsewhere. Possibly China, India or elsewhere in the far east. It will be produced using coal (coke) and probably less efficiently than we produce it. There will therefore be at least as much CO2 emitted globally and possibly more.
We could look to producing steel in the UK using hydrogen as the reducing agent and a combination of hydrogen and electricity as the heat source. If we had sufficient non carbon electricity, or possibly even if we had not, this would reduce global CO2 emissions. It would also keep the jobs in the UK and reduce our dependence on China and other similar countries. Why are we not doing this?