
Consultation question: Considering the information presented in this call for evidence paper, and your own knowledge and experience, what are your views on the extraction of coal in Scotland?
Our response: The Welsh Government's most recent policy statement on coal should provide a starting point for the Scottish Government to build upon (https://gov.wales/coal-policy-statement-html) in developing its own policy, as there are clear and relevant parallels between both Governments.
Both Wales and Scotland has a long legacy of suffering the localised impacts of environmental blight and hazardous conditions of coal mining, with nearby communities rarely seeing a significant share of the economic benefits. Wales is still littered with unrestored or poorly restored coal mines. It was reported that only this year are the final abandoned coal mines in Scotland being restored - again, often to revised, lower standards that what was promised nearby communities due to insufficient restoration bonds.
Now more is known about climate change, both Wales and Scotland have led the way in developing progressive policies and practice to realise their ambitious targets. This cannot include viably include coal, which is worse in CO2 emissions than natural gas and oil in its conversion factor to energy. The EIA Pathways to Net-Zero report make this very clear, underscoring that no new coal mining for any purpose can be part of a pathway to Net-Zero by 2050.
A critical part of that report is no new coal mining for any purpose. The report goes further to explicitly include coking coal for steel in this prohibition. Port Talbot Steelworks in South Wales and British Steel in England are the 2nd and 3rd largest single-site sources of CO2 in the UK - because they burn coal. Any policy that differentiates between the extraction of coal for energy production and coal for steel production, ignores this growing threat to meeting climate targets across the world. It would also ignore the rapidly escalating developments around the world in decarbonising the steel industry. Green steel is on its way, with the first delivery of commercial quantities made from Sweden in 2021. Unfortunately, once investors have opened a coal mine, they will seek return on that investment and find alternative markets for the coal, or laggard steelworks that still rely on coal in the future. So permitting new coal mining for steel will prop up the biggest polluters and discourage transition to new technology and practices.
There is no viable future for any of us that relies on coal to get us there. Scotland should be using its just transition fund to skill its inhabitants in the industries of the future, not ploughing people into the industries that destroy that future.

The direct use of coal as a feedstock (not just energy) is particularly significant in China, where coal is used extensively in coal to gasification plants to produce chemicals such as methanol, ammonia, and…

This nature was photographed around 50 metres from the edge of the Glan Lash opencast coal mine in Ammanford, South Wales. It shows the thriving ecosystems surrounding the Glan Lash opencast coal mine which has remained dormant since 2019…

In February, CAN gave oral testimony to the Climate Change, Energy, and Infrastructure Committee (CCEIC) on the Disused Mine and Quarry Tips (Wales) Bill…

Coal Action Network was invited to attend Westminster where we gave evidence to the Welsh Affairs Committee in their inquiry about the environmental and economic legacy of Wales’ industrial past, alongside Friends of the Earth Cymru. This inquiry was opened in…

16 years of opencast coal mining in Ffos-y-fran has generated colossal overburden mounds, also known as slag heaps or coal tips. There are three coal tips, with the third being the largest, and cumulatively accounting for 37 million cubic metres of colliery spoil, rocks, and soil…

We were invited for the second time to give oral evidence to the Climate Change, Environment, and Infrastructure Committee of the Welsh Parliament (Senedd) on 05th February 2025. We shared the panel with Haf, Director of FOE Cymru, to provide our opinion on the weaknesses, strengths…
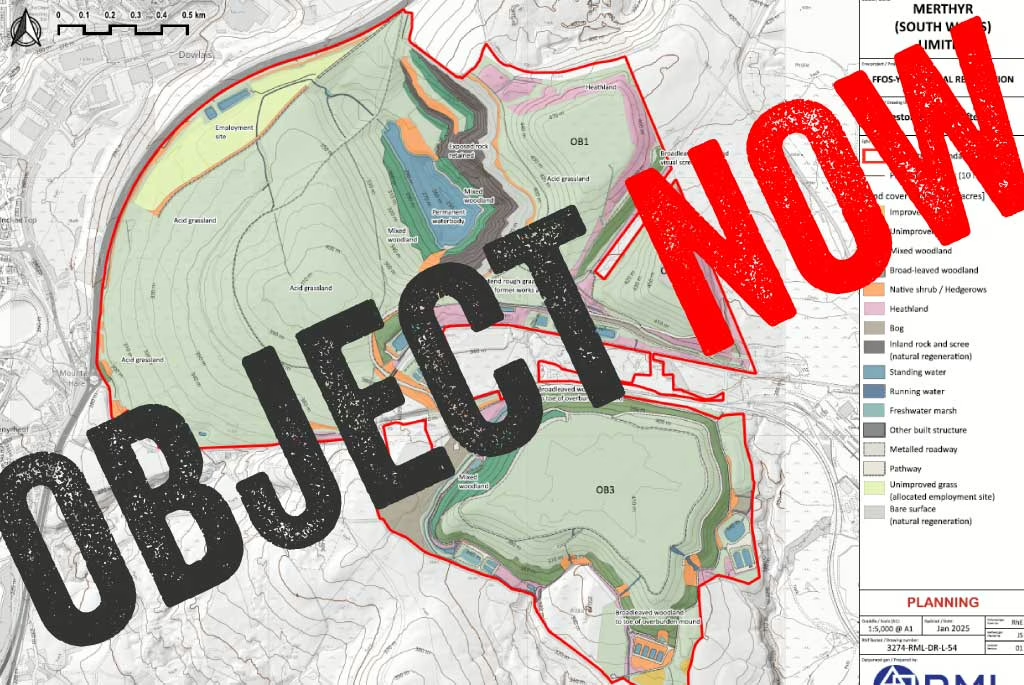
Merthyr (South Wales) Ltd mined for over a year illegally after planning permission for the Ffos-y-fran opencast coal mine ended in September 2022. During that year, it made record-breaking profits due to sanctions on Russia and other factors driving up the price of coal. But rather than using some of the profits from that ill-gotten coal…

MSW claims “It was established that there are insufficient funds available to achieve the 2015 restoration strategy and therefore an alternative scheme is required.” (EIA Scoping Report, July 2024)… To our knowledge, there has been no evidence submitted by MSW that it cannot fund the full restoration it is contracted to undertake…

The UK Government launched a consultation on a limited review of the National Planning Policy Framework (NPPF) for 8 weeks from 30 July to 24 September 2024. The NPPF is an influential document that shapes planning decisions and priorities across England. It is periodically updated by the Government, following a public consultation…
Germany has followed Sweden with turning to electrical sources of heating in steel production. It is both cheaper and much cleaner. Electricity is the future.