
What is the Lloyd’s of London?
Firstly, it’s nothing at all to do with Lloyd’s PLC, the bank – they’re not great either, but that’s another story.
Lloyd’s of London is a large insurance corporation with an HQ in London but trade insurance globally. In its own words, Lloyd’s of London “oversees and supports the Lloyd’s market, ensuring it operates efficiently and retains its reputation as the market of choice for specialist insurance and reinsurance risk.” You can watch Lloyd’s of London’s very corporate video explaining what they do.
What is “Lloyd’s marketplace”?
Insurance companies use Lloyd’s of London’s marketplace much like sellers use eBay’s website. Just as eBay supports bidding between buyers and sellers, so does Lloyd’s of London, employing over 200 brokers to match insurance customers with insurance companies. And just like eBay, Lloyd’s of London offers some form of guarantee for insurance bought via their marketplace, encouraging trades through to be made through it.
What is Lloyd’s of London's connection to Adani and West Cumbria coal mines, and fossil fuels
Lloyd’s of London marketplace is in the top 4 for insuring climate-wrecking fossil fuel projects around the world. Lloyd’s of London’s marketplace is particularly attractive to large fossil fuel projects as Lloyd’s has a reputation for getting high-risk projects insured that other insurance companies won’t touch. One way it does this is by splitting an insurance policy, and spreading the risk, between insurance companies using their marketplace. This amounts to an insurance for climate chaos as it’s only with insurance that companies can take the financial risks to dig new coal mines, build new tar sand pipelines, and explore new gas and oil fields.
Lloyd’s of London has refused to rule out allowing Adani’s Carmichael coal mine in Australia or the West Cumbria coal mine in the UK to obtain insurance via their marketplace. If Adani’s Carmichael coal mine gets insurance and goes ahead, it would open up one of the world’s biggest coal deposits contributing to a climate catastrophe.
What is Lloyd’s of London doing to prevent their contribution to climate change?
Not much, and definitely not enough.
Lloyd’s of London have only committed to a policy of greenwash that is incompatible with our climate crisis, continuing to insure risky projects that no one else will touch. So far Lloyd’s of London has committed to asking insurers operating in their marketplace to stop insuring tar sands, thermal coal mines, and Arctic exploration, phasing this out by 2022. But ‘reinsurance’ for these worst offenders is allowed up until 2030.
This also leaves a huge range of climate-wrecking projects free to continue insuring their risk via Lloyd’s of London marketplace with no policy at all to discourage it. In practice, this means the planned West Cumbria mine could be insured via Lloyd’s of London marketplace as it intends to mine ‘coking coal’, not ‘thermal coal’, although both are eventually burned, producing similar emissions.
What more could Lloyd’s of London marketplace do to prevent their contribution to climate change?
Lloyd’s of London could most simply ban all fossil fuel insurance trading via their marketplace. Their own statement clearly indicates this would be possible; “Lloyd’s publishes minimum standards and monitors compliance with those minimum standards. Lloyd’s by-laws also set out a number of rules with which market participants are required to comply”.
Fossil fuel projects only amount to around 5% of Lloyd’s of London’s marketplace insurance trades, so the company would still have a future without selling out ours.
What would be the impact if Lloyd’s of London ruled out fossil fuel insurance?
Some of the fossil fuel projects would source insurance from other providers and marketplaces, but many using Lloyd’s of London marketplace have failed to secure insurance elsewhere—Lloyd’s of London is sometimes their last chance. Let’s not give it to them.
Insurance providers also look to one another in setting their policies, so if Lloyd’s of London drops fossil fuel insurance, it is likely other insurance traders and providers will too—with a bit of encouragement.
Insurance might not be the sexiest subject, but it is a very vulnerable link in the chain needed to start and continue these huge climate-wrecking projects. It’s time Lloyd’s of London take responsibility for the role its insurance marketplace has in our collective future.
What is an insurance policy?
A contract that a company or individual takes out with an insurer to protect them against specific risks in ways that are agreed and noted in the contract.
What is ‘claims made’ insurance?
Type of insurance policy that will cover insurance claims made whilst the insurance policy is in force – even if the event leading to that insurance claim happened before that insurance policy came into force.
What is ‘claims occurring’ insurance?
Type of insurance policy that will cover insurance claims for events that occurred whilst the insurance policy is in force – even if the claim for it happens after the insurance policy stopped being in force.
No related insurance:
They don't insure coal mines e.g. they just cover travel insurance.
What is ‘run-off’ insurance:
AKA: Not 'live' insurance. Type of insurance policy that comes into effect when a company stops trading. So, any claims made under it will relate to events that happened before the company stopped trading and the policy started. This is used by companies that had ‘claims made’ insurance, and want insurance in case anyone takes action against them after the company for the period of time after they stopped trading but are still liable.
Want to know more?

Coal Action Network is proud to present our 2026 manifesto for Wales. With the Senedd elections taking place in May this year, Wales stands at a decisive moment. For over a century, coal has shaped Welsh landscapes, communities, and politics. Today, Wales has the opportunity to shape something very different…

As part of our Politics Unspun series we are unpacking politicians’ public comments on coal to challenge any misleading or incorrect messages. Todays’ focus is on comments made during a Westminster Hall debate in December 2025 about the oil refining sector. During the debate, Lee Anderson MP made some statements about coal…

The Government is reforming planning policy in England and thanks to thousands of our supporters asking for an end to coal extraction in the last consultation in 2024, they are now recommending that planners “should not identify new sites or extensions to existing sites for peat or coal extraction”…
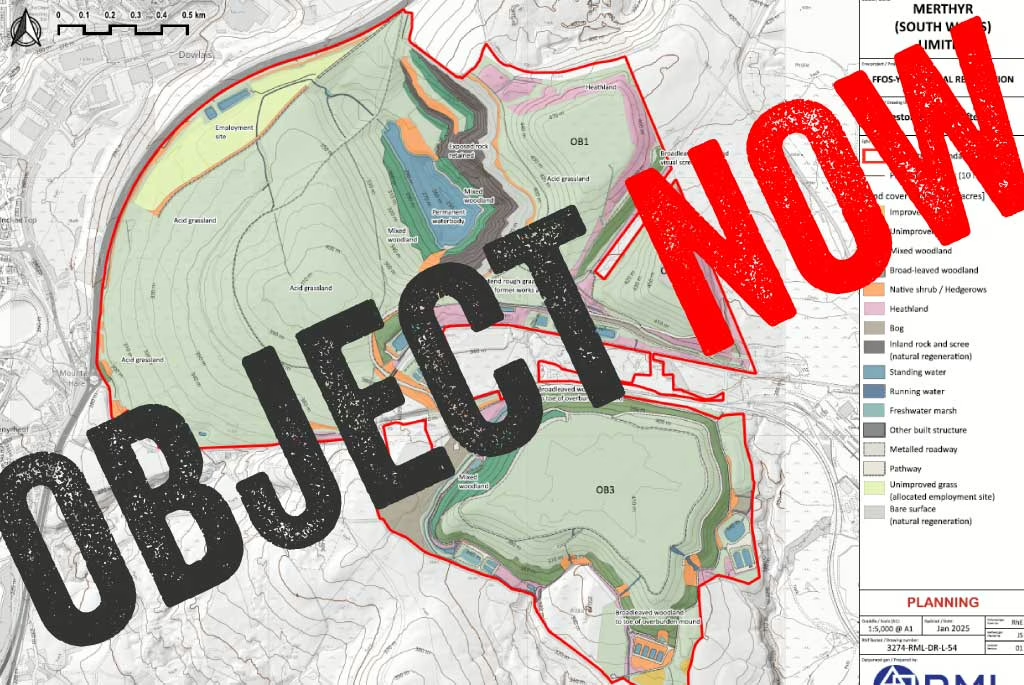
Merthyr (South Wales) Ltd mined for over a year illegally after planning permission for the Ffos-y-fran opencast coal mine ended in September 2022. During that year, it made record-breaking profits due to sanctions on Russia and other factors driving up the price of coal. But rather than using some of the profits from that ill-gotten coal…

In November 2024, the new UK Government announced its intention to legislate a ban of new coal mining licences – which we welcomed. Over a year later, the legislation is yet to be introduced, and the Government is not planning to include all types of extraction…

The UK steel and cement sectors (and to a lesser extent, bricks) are the largest users of coal following the closing down of the UK’s last coal-fired power station in September 2024. Check out our coal dashboard for our most recent coal stats including an industry break-down. We support the UK Government’s commitment to ban…

The steel industry produces 9-11% of the annual CO2 emitted globally, contributing significantly to climate change. In 2024, on average, every tonne of steel produced led to the emission of 2.2 tonnes of CO2e (scope 1, 2, and 3). Globally in 2024, 1,886 million tonnes (Mt) of steel were produced, emitting…

Last month we worked with Members of Parliament from various parties on a Westminster Hall debate about coal tip safety and the prohibition of new coal extraction licences. The debate happened 59 years and one day after the Aberfan tragedy which killed 116 children and 28 adults…

Successful, at-scale, examples already exist of cement works burning 100% fuel alternatives to traditional fossil fuels, including pilot projects using combinations of hydrogen and biomass (UK) and hydrogen and electricity (Sweden). Yet, innovations such as use of hydrogen and kiln electrification are…