Demand nature be restored to Ffos-y-fran opencast site
February 28th 2025
Merthyr (South Wales) Ltd mined for over a year illegally after planning permission for the Ffos-y-fran opencast coal mine ended in September 2022. During that year, it made record-breaking profits due to sanctions on Russia and other factors driving up the price of coal. But rather than using some of the profits from that ill-gotten coal…

We investigate mining company’s ‘missing’ millions
February 6th 2025
MSW claims “It was established that there are insufficient funds available to achieve the 2015 restoration strategy and therefore an alternative scheme is required.” (EIA Scoping Report, July 2024)… To our knowledge, there has been no evidence submitted by MSW that it cannot fund the full restoration it is contracted to undertake. On the contrary, MSW’s most recent, publicly available, financial statement on Companies House says “Full account has been taken for funding the restoration obligation in the future costs and cash flows”…

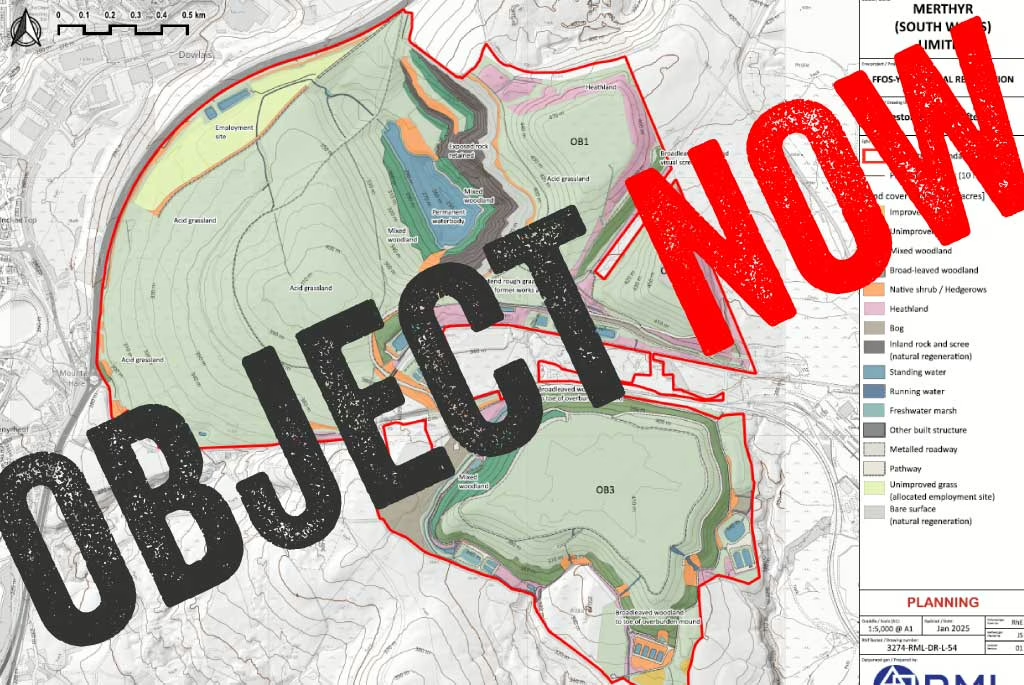
UK Government: is the left hand speaking to the right hand?
January 8th 2025
The UK Government launched a consultation on a limited review of the National Planning Policy Framework (NPPF) for 8 weeks from 30 July to 24 September 2024. The NPPF is an influential document that shapes planning decisions and priorities across England. It is periodically updated by the Government, following a public consultation…

We expose company’s misleading claims
January 6th 2025
Bryn Bach Coal Ltd attempts to present the anthracite coal it wishes to extract from an expansion of Glan Lash as a unique and scarce commodity that is needed for water filtration, bricks, and graphite, and would therefore be too valuable to burn. Yet, visiting Energybuild Ltd’s…

Major wins of 2024
December 28th 2024
Over the past year, we’ve secured some massive victories. By taking part in our digital actions, supporters sent over 26,000 messages to the UK Government, MPs, Welsh Senedd members, Councillors, and companies to help consign coal to the history books in the UK…

Disused Mine and Quarry Tips (Wales) Bill
December 23rd 2024
The Disused Mine and Quarry Tips (Wales) Bill (‘the Bill’) was prompted by a series of coal tip landslides that occurred in Wales following storms’ Ciara and Dennis in 2020, including a major landslide of a disused coal tip in Tylorstown…

Under pressure: Europe’s largest mining investment conference
December 20th 2024
As B Labs doesn’t seem bothered was the public says, we asked supporters to contact other B Corps – who are effectively B Labs customers. Almost 20,000 emails were sent to over 60 B Corp status companies, asking them to take a stand with us…

Coal tip remediation – not coal tip mining
November 27th 2024
The Welsh Government’s long-awaited Bill is expected to be presented to the Senedd before the end of 2024. The very recent Cwmtillery tip slip will make this Bill a more politically charged issue. It will also raise scrutiny over whether measures…

Türkiye’nin Kömür Kullanımına Devam Etmesi
November 19th 2024
Kömür Eylem Ağı (Coal Action Network), 2024 yılında Türkiye kömür endüstrisini araştırdı. Bu makalede, bulgularımız ve Türkiye’deki kömür, hava kirliliği, Rusya savaşı ile karbonsuzlaştırma arasındaki ilişkiler inceleniyor.










